Musk allegedly said there's a 70% chance for him to move to Mars.
However, Klevius warns him that the ISS strains of Enterobacter were 79% likely to cause illness.
In Demand for Resources (1992:31, ISBN 9173288411) in a discussion about the olfactory organ that we call the brain, Klevius warned for (over)hygien being the most important factor causing allergies etc. Apart from pure logic and knowledge about super bugs etc., Klevius had an other experience with his newborn child who had a bleeding navel that the nurses repeatedly cleaned with disinfection and asked us parents to do the same at home. However, we didn't and the navel was fine next day.
Newborn babies before modern hygiene got better used to their bacterial environment.
So what went wrong on ISS was that they didn't make the toilet dirty enough on Earth, in other words, surrounding it with a normal protective flora of germs. We don't live on oxygen and food alone, we need also to be embedded in a protective symbiotic "bubble" of a multitude of various germs.
Compare this to how Pygmies are protected against Ebola whereas the Bantu (i.e. Eurasian late comers to Central Africa
msee Klevius out-of-Asia theory below and on the web) are less well prepared.
Something similar will happen on Mars.
Also consider what Klevius wrote in
Klevius wrote:
Wednesday, August 3, 2016
Peter Klevius 1992 (and developing* ahead of others) theory on human evolution - and guts with brains
"Ornamented" bacteria colonies (copyright* Peter Klevius - but do feel free to cite)
* Klevius texts are usually way ahead of the time they're written down, i.e. truly original. However, precisely because of this they rarely get the attention they deserve. Moreover, due to general time-bound alterations in the discourse at stake, not to mention particular alterations in attitudes and values, connotations may vary and make reading more difficult, especially if the text was progressive for its time. However, Klevius texts can usually be safely "time-translated" because central concepts are thoroughly presented at the time of writing (this is the delicate balancing act Klevius mentions in the foreword to his book, i.e. connecting associations between author and reader. This is also why Klevius loves to "brag" by challenging readers to find serious thoughts by Klevius anywhere else earlier than Klevius. A good example is EMAH - the Even More Astonishing Hypothesis on human cognition. An other is sex segregation and the social state, a third one being Klevius analysis of the so called Negative Human Rights from a sex neutral point of view, a fourth is Klevius classification of human societies not according to what they do but what they want (see e.g. chapter Khoe, San, and Bantu in Demand for Resources), a fifth being an analysis of Freud, his daughter, and Margaret Mahler, from a sex segregation and "motherhood guilt" perspective (see e.g. Pathological Symbiosis), and a sixth could be Klevius analysis of the social state (see e.g. Angels of Antichrist), and a seventh... There are also loads of other minor discoveries made by Klevius, such as, for example, the crucial connection between Freud's emerging psychoanalysis and Caton's much earlier discovery of electrical brain activity, and a PhD thesis on Heterosexual attraction and the failure of feminist theory (compare Klevius web museum from 2007, klevius.info, and Gametes have nos sexes), etc. etc.,All organisms, including us, are differently equipped bacteria colonies. The first such bacteria colonies probably evolved from bacteria "mats" that rolled into a membrane through which they could communicate nutrition/metabolism. This evolutionary step resembles Klevius view on how RNA much earlier cloaked itself in a protein capsid. Viruses may have evolved from self-replicating molecules that later on created the cells which conventionally have been seen as predecessors for virus. Klevius first got the idea as a late teenager when he first heard about prions, i.e. self-convoluting proteins. He wondered whether it could be possible that prions at some point wrapped around loose RNA, hence creating the first viruses. "Pre-life" amino acids capable of forming foldable proteins would have made this possible. RNA would hence constitute a proto-DNA.
When colonies of one-cell organisms got an outer membrane that could communicate food supply and disposal (incl. disposal of parts of itself) the next step was to create independent movement etc. This last stage led to a diversity of different solutions and approaches depending on environmental circumstances.
So in short, we are walking and thinking slaves of our guts. And the brain and its intelligence that we are so proud of (as long as it's not Klevius brain, of course) is created for the purpose of feeding our guts. When it produces tech, innovations, art etc., this is just a byproduct of its main duty to serve the gut bacterias.
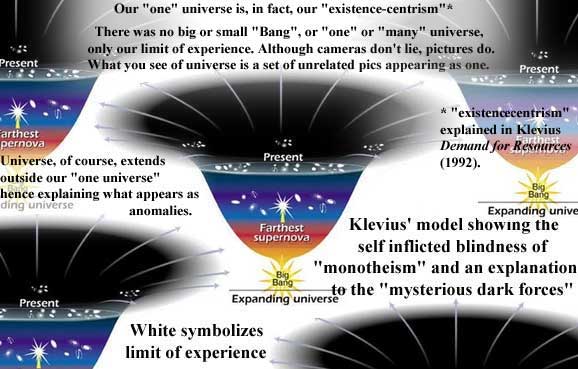
Existencecentrism in an endless unimaginable Universe where the very question "why are we here?" resides (with all its connotations etc) inside existencecentrism, hence outside the very realm that it's supposed to address.
In Demand for Resources (1992, ISBN 9173288411) - where Klevius called this realm the unreachable - he sketched evolution and our position with a tool called 'existencecentrism', i.e. a fundamental bias that we can change but never get rid of. Klevius thought this axiomatic statement could stand as a basis for hunting down lower level bias in science. This approach was well received 1980 by George Henrik von Wright (the Finland-Swedish philosopher who succeeded Ludvig Wittgenstein at Cambridge) and was first published in the Finland-Swedish Hufvudstadsbladet 1981. Payment was Fmk 500.00 (so quite a distance from e.g. Hillary Clinton who gets enormous sums for opening her mouth in accordance to her muslim sharia masters).
According to Klevius (1981, 1992) the basic element in our understanding of Universe is motion that causes evolution and devolution in a causal stream of changing complexities. This understanding, however, also locks itself on our metaphysical explorations.
No wonder the "big bang" concept was invented by a cleric.
Klevius wrote:
Monday, January 9, 2012
The ridiculous idea about "one god" hampers CERN/LHC
Universe doesn't have limits - nor is it endless
In my book Demand for Resources (Resursbegär1992:21-22) I pointed out not only the dangers of such a senseless "model" as "Big Bang" but also how this "model" is trapped in a "monotheistic" view demanding "creation", i.e. a "starting point". Not only is such a "starting point" conceptually impossible (apart from its very obvious other limitations, e.g. how do you "bang" in "nothing") but it also fatally misdirects research focus because it assumes "a universe" or "the universe" where there's only universe.
A time trip back towards the "Big Bang" would only reveal a continuing growth of neighboring "universes". The space/time continuum and warping would make the "Big Bang" model laughable.
To my surprise I've noticed how many decently minded people seem to have great difficulties understanding how the great distances and the great limitations caused by the speed of light constant, warps every effort to take even quite small thought steps, say for example only within our own tiny galaxy.
Cameras never lie - pictures do!
All space cameras, from our own eyes to the Hubble space telescope and its follow-ups, have in common that they don't take pictures of space but of themselves, i.e. photo reactions on the retina, CCD etc. These reactions are then interpreted by our knowledge. However, to describe such reactions as a picture of space is extremely misleading.Kleius wrote:
Friday, April 5, 2013
Where's the star and where were you?
The illusion of a Universe
A ten billion year old supernova has been discovered. It means it died ten billion years ago, i.e. 5.5 billion years before our Sun was born.
The black area on the pic above corresponds to the white area on Klevius' Origin of Universe pic.
The light from the farthest objects detectable by Hubble and other cameras (incl. radio waves etc), i.e. more than 13 billion years ago, marks the end of our capabilities, not the end of Universe. Because there is no "end" or "beginning". These terms are oxymorons and semantically absurd.
So next time you take a look at the stars do consider what you don't see.
Klevius wrote:
Thursday, March 15, 2012 (with some random updates)
The Red Deer Cave people add more evidence for Klevius’ ape/homo hybridization theory
The irrefutable art track in Northern Eurasia (see map below) has no contemporary equivalent in other parts of the world. Based on what we know now it had no fore bearers whatsoever in any period of time. Moreover, it seems that there was even a decline before "civilizations" started tens of thousands of years later! Yet Klevius seems to be the only one addressing this most interesting (besides genetics) fact! According to Klevius (and no one else so far) the new and more efficient brain evolved in a jungle environment (SE Asia?) and spread up until meeting with big headed Neanderthals hence creating the modern human who later spread and dissolved with archaic homos. In this process Homo erectus was most probably involved as well.
Updated info about the origin of Klevius' theory
Keep in mind that mainland SE Asia possibly harbored physically truly modern humans already before the time range (12,000/18,000 ybp - 98,000 ybp) of the Homo floresiensis remains in the Flores cave.Liujiang, SE China (est. 100,000-140,000ybp)
If this Liujiang skull had been found in Africa or Mideast Wikipedia and other media would be overfilled. But this is all you get now (summer 2015 update) from Wikipedia about this extremely important skull:
The Liujiang skull probably came from sediment dating to 111 000 to 139 000 which would mean it's older than the oldest Homo floresiensis remains on Flores. Nothing even remotely close to this modern skull has ever been found in Africa, Mideast or Europe this early. In other words, we have the extremely archaic looking Red Deer Cave people 100,000 years after this extremely modern looking Liujiang population at approximately the same region. Even the least probable estimate of 70,000 bp would make Liujiang more modern looking than anything else.
Also compare Lake Mungo remains in Australia with an mtDNA that differs completely from ours (incl. Australian Aborigines). Sadly the remains have been kept out of further research because of stupid* "Aboriginal"(?!) greed (for the purpose of making certain people more "special" than others for no good reason at all (also compare the ridiculous Kennewick man controversy). Does it need to be said that the Mungo remains are as far from Australian Aborigines in appearance as you can imagine. However, according to Alan Thorne, 'Mungo could not have come from Africa as, just like Aboriginal Australians don't look like anybody from Africa, Mungo Man's skeleton doesn't look like anybody from Africa either. LM3 skeleton was of a gracile individual, estimated stature of 196 cm, which all sharply contrast with the morphology of modern indigenous Australians. Compared to the older Liujiang skull Mungo man had a much smaller brain.
* There's no way anyone can state who was "first" in Australia - and even if there was, then there's still no way of making any meaningful connection to now living people.
In Demand for Resources (1992:28 ISBN 9173288411) in a chapter about human evolution, Peter Klevius used only one example, the remarkable Jinniushan skeleton/cranium:
In northern China near North Korean border an almost complete skeleton of a young man who died 280,000 years ago. The skeleton was remarkable because its big cranial volume (1,400cc) was not expected in Homo erectus territory at this early time and even if classified as Homo sapiens it was still big. The anatomically completely modern human brain volume is 1,400 cc and appeared between 50-100,000 years ago. One may therefore conclude that big brain volume by far predated more sophisticated human behavior (Klevius 1992:28).
Today, when many believe the skeleton is female, the brain size becomes even more remarkable.
Updated map. Peter Klevius is deeply ashamed of not having removed the "African savanna" earlier. It has absolutely nothing to do with human evolution - only with the progression of already evolved hominines from outside Africa. At this point of knowledge it's beyond doubt that all main evolutionary stages in human evolution were impossible in Africa. It's senseless charlatanism to even consider "climate etc. changes" as enough to isolate bipedal hominines long enough for evolutionary purpose. However, what's even more embarrassing for the anthropological "community" is that Peter Klevius still seems to be the only one daring to point it out.
Most "mysteries" in genetics disappear by abandoning OOA and changing direction of HSS evolution. Only South East Asia offered a combination of tropical island/mainland fluctuations needed to put pressure on size reduction paired with evolutionary isolation in an environment where only those survived who managed to shrink their heads while keeping the same intelligence as their mainland kins with some double the sized brain. Homo floresiensis is evidence that such has happened there.
Denisovan is an extinct species of human in the genus Homo. In March 2010, scientists announced the discovery of a finger bone fragment of a juvenile female who lived about 41,000 years ago, found in the remote Denisova Cave in the Altai Mountains in Siberia, a cave which has also been inhabited by Neanderthals and modern humans. Two teeth and a toe bone belonging to different members of the same population have since been reported.
Analysis of the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) of the Denisovan finger bone showed it to be genetically distinct from the mtDNAs of Neanderthals and modern humans. Subsequent study of the nuclear genome from this specimen suggests that this group shares a common origin with Neanderthals, that they ranged from Siberia to Southeast Asia, and that they lived among and interbred with the ancestors of some present-day modern humans, with about 3% to 5% of the DNA of Melanesians and Aboriginal Australians deriving from Denisovans. DNA discovered in Spain suggests that Denisovans at some point resided in Western Europe, where Neanderthals were thought to be the only inhabitants. A comparison with the genome of a Neanderthal from the same cave revealed significant local interbreeding, with local Neanderthal DNA representing 17% of the Denisovan genome, while evidence was also detected of interbreeding with an as yet unidentified ancient human lineage. Similar analysis of a toe bone discovered in 2011 is underway, while analysis of DNA from two teeth found in layers different from the finger bone revealed an unexpected degree of mtDNA divergence among Denisovans. In 2013, mitochondrial DNA from a 400,000-year-old hominin femur bone from Spain, which had been seen as either Neanderthal or Homo heidelbergensis, was found to be closer to Denisovan mtDNA than to Neanderthal mtDNA.
Little is known of the precise anatomical features of the Denisovans, since the only physical remains discovered thus far are the finger bone, two teeth from which genetic material has been gathered and a toe bone. The single finger bone is unusually broad and robust, well outside the variation seen in modern people. Surprisingly, it belonged to a female, indicating that the Denisovans were extremely robust, perhaps similar in build to the Neanderthals. The tooth that has been characterized shares no derived morphological features with Neanderthal or modern humans. An initial morphological characterization of the toe bone led to the suggestion that it may have belonged to a Neanderthal-Denisovan hybrid individual, although a critic suggested that the morphology was inconclusive. This toe bone's DNA was analyzed by Pääbo. After looking at the full genome, Pääbo and others confirmed that humans produced hybrids with Denisovans.
Some older finds may or may not belong to the Denisovan line. These includes the skulls from Dali and Maba, and a number of more fragmentary remains from Asia. Asia is not well mapped with regard to human evolution, and the above finds may represent a group of "Asian Neanderthals".
Jinniushan and Floresiensis - the keys to Denisovan and the truly modern humans
Jinniushan had a bigger brain than anything in contemporary Africa
In Demand for Resources (1992:28 ISBN 9173288411) in a chapter about human evolution, Peter Klevius used only one example, the remarkable Jinniushan skeleton/cranium:
In northern China near North Korean border an almost complete skeleton of a young man who died 280,000 years ago. The skeleton was remarkable because its big cranial volume (1,400cc) was not expected in Homo erectus territory at this early time and even if classified as Homo sapiens it was still big. The anatomically completely modern human brain volume is 1,400 cc and appeared between 50-100,000 years ago. One may therefore conclude that big brain volume by far predated more sophisticated human behavior (Klevius 1992:28).
Today, when many believe the skeleton is female, the brain size becomes even more remarkable.
Since 1991 when Klevius wrote his book much new information has been produced. However, it seems that the Jinniushan archaic Homo sapiens still constitutes the most spectacular anomaly (together with Homo floresiensis) in anthropology. So why did Klevius pick Jinniushan instead of one of the more fashionable human remains? After all, Klevius was a big fan of Rchard Leakey (he even interviewed him in a lengthy program for the Finnish YLE broadcasting company) and there was a lot of exciting bones appearing from the Rift Valley.
In the 1980s Klevius paid special attention to Australian aborigines and African "bushmen" and noted that the latter were mongoloid in appearance (even more so considering that todays Khoe-San/Khoisan are heavily mixed with Bantu speakers). But mongoloid features are due to cold adaptation in the north and therefore the "bushmen" had to be related to Eurasia. Klevius soon realized that the Khoisan speakers had moved to the southern Africa quite recently as a consequence of the so called Bantu expansion. More studies indicated that the "bushmen" had previously populated most of east Africa up to the Red Sea and beyond.
So the next step for Klevius was to search for early big skulled human remains in the mongoloid northern part of Eurasia. And that search really paid off.
This happened more than 20 years before the discovery of the Denisova bracelet and the human relative Denisovan in Altai.
Klevius book Demand for Resources (1992) in which these thoughts about mongoloid traits were published also predates Floresiensis with more than a decade.
Peter Brown (world famous for discovering/defending Floresiensis in 2004 and who had big trouble getting his PhD accepted because of a biased supervisor/institution): What makes Dali, as well as Jinniushan (Lu, 1989; Wu, 1988a), particularly important is that both of their facial skeletons are reasonably complete. This is an unusual situation in China as the only other middle Pleistocene hominids to have faces in China are the Yunxian Homo erectus (Li and Etler, 1992), which are both very distorted. Originating in the pioneering research of Weidenreich (1939a, 1939b, 1943) at Zhoukoudian, there has been strong support by Chinese Palaeoanthropologists for evolutionary continuity between Chinese H. erectus and modern humans in China. It has been argued that this is most clearly expressed in the architecture of the facial skeleton (Wolpoff et al., 1984). East Asian traits have been argued to include lack of anterior facial projection, angulation in the zygomatic process of the maxilla and anterior orientation of the frontal process, pronounced frontal orientation of the malar faces, and facial flatness. While some of these traits may occur at high frequency in modern East Asians (cf Lahr, 1996) they are not present in late Pleistocene East Asians, for instance Upper Cave 101 and Liujiang (Brown, 1999), or more apparent in Dali and Jinniushan than archaic H. sapiens from Africa or Europe. Recently there has been a tendency to link a group of Chinese hominin fossils, including Dali, Maba, Xujiayao, and Jinniushan, previously considered by some researchers to be "archaic Homo sapiens", with the Denisovians (Reich et al. 2010; Martinón-Torres et al. 2011) (http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v468/n7327/full/nature09710.html). However, apart from a few teeth, the Denisovians are only known from palaeo DNA. There is also a great deal of anatomical variation in the Chinese "archaic Homo sapiens" group. It will be interesting to see how this plays out over the next decade, or so.
Klevius: It turns the conventional anthropological map on its head!
For a background to Klevius' theory see previous postings and Out of Africa as Ape/Homo hybrids and back as global Mongooids
First and third from the left are Red Deer Cave people 14,300-11,500 years ago. Second and fourth the so called Venus from Brassempouy in France 25-26,000 years ago. The last pic is a reconstruction of a 1.9 Million year old Homo rudolfiensis skull. They all had flat broad cheeks, no chin and rounded forehead.
From the left: Red Deer Cave, Sami, Cro-Magnon
Was the sculptural portrait of Venus of Brassempouy made because she looked so different from Cro Magnon? Was she kept as a pet or something by her Cro Magnon captors?
There were certainly completely different looking modern humans living in Eurasia side by side some 26,000 years ago. And the only way to make sense of these enormous differences is Klevius hybridization theory, i.e. that the modern brain came from small ape-like creatures (compare the "scientists" who didn't believe that the small Homo floresiensis brain could be capable of tool-making, fire-making etc..
Venus of Brassempouy, one of the world's oldest real portrait
(this one slightly retouched by Klevius)
 The
Red Deer Cave people, discovered in southern China and who lived some
14,300-11,500 years ago had long, broad and tall frontal lobes behind
the forehead, which are associated with personality and behavior.
However, they also express prominent brow ridges, thick skull bones,
flat upper face with a broad nose, jutting jaws and lack a humanlike
chin. Their brains were smaller than modern humans and they had large
molar teeth (just like Denisovan), and short parietal lobes at the top
of the head (associated with sensory data). According to Curnoe, "These
are primitive features seen in our ancestors hundreds of thousands of
years ago".
The
Red Deer Cave people, discovered in southern China and who lived some
14,300-11,500 years ago had long, broad and tall frontal lobes behind
the forehead, which are associated with personality and behavior.
However, they also express prominent brow ridges, thick skull bones,
flat upper face with a broad nose, jutting jaws and lack a humanlike
chin. Their brains were smaller than modern humans and they had large
molar teeth (just like Denisovan), and short parietal lobes at the top
of the head (associated with sensory data). According to Curnoe, "These
are primitive features seen in our ancestors hundreds of thousands of
years ago".  This Cro Magnon could have been the captor of Venus of Brassempouy.
Compare e.g. his protruding chin with the retracting one on Venus of
Brassempouy. And keep in mind that the human chin has been an elusive
and quite recent feature in human evolution. The delicate features we
used to attribute to anatomically modern human while simultaneously
attributing high intelligence may, in fact, not be connected at all.
Slender and delicate skeletal features are not always connected with
high cultural achievement. Quite the opposite when looking at skeletal
remains outside the Aurignacian area..
This Cro Magnon could have been the captor of Venus of Brassempouy.
Compare e.g. his protruding chin with the retracting one on Venus of
Brassempouy. And keep in mind that the human chin has been an elusive
and quite recent feature in human evolution. The delicate features we
used to attribute to anatomically modern human while simultaneously
attributing high intelligence may, in fact, not be connected at all.
Slender and delicate skeletal features are not always connected with
high cultural achievement. Quite the opposite when looking at skeletal
remains outside the Aurignacian area..Klevius comment: Consider the circumstances. Small population and, at some stage, no previous "teachers". This northern part of the Aurignacian struck almost out of the blue unles you also consider the Denisova bracelet.
This extremely complicated to manufacture stone bracelet was made by the ape-like "non-human(?) Denisovan hybrid in Siberia >40,000 years ago by utilizing a drilling technology, comparable to modern machines, according to the researchers who found it.
According to Klevius' theory we got our modern brain intelligence from hybridization with apes (Pan?). These creatures were small and apelike although bipedal. When they moved north they encountered cold adapted Homos with large skulls. This combination created the most intelligent people ever on the planet. However, when this extremely small population began expanding it dissolved with the big headed but stupid Homos hence empowering their intelligence while diluting its own. The mix became today's humans.
Homo floresiensis on Java (i.e. north of the Wallace line as opposed to thise found on Flores) may be, and the Denisovans in Siberia are variants on this hybrid path.
"Racial" distribution in accordance with Klevius' "Out of Siberia and back to Africa" theory (aka "Out of Africa as pygmies and back as global mongoloids"
Mongoloids and Australoids are the races most distant from each other because whereas Africa had a strong back migration of mongoloids Australia due to its location came to be less involved. This is also why the so called Caucasoid race (in a broad sense) came to populate what in Klevius terminology is called the "bastard belt" (the grey area on the map).
The senseless Mideastern "creation out of nothing" ideology got popular only because it boosted patriarchal sex apartheid (Adam created by "god" and woman created from Adam).
The incredibly stupid (see postings below) "Out of Africa" term only competes with the equally misleading and stupid "Big Bang" term - see Klevius new blog on the Origin of Universe (note that there's no 'the' in front of universe).
M130
Genetic traces of Denisovan
Klevius' human evolution formula from hot to cold
Chimp/Homo hybridization (FOXP2 variant) + meeting/mixing with Eurasian Homos = Denisovan (Floresiensis?) and leaves an early but misleading genetic Africa label due to the back and forth movement between Eurasia and Africa.
Denisovan (Floresiensis?) gets a better packed brain in island Indonesia through sea level isolation. Later on the opposite effect releases some of them into Asian mainland.
In summary, the oldest African genes are not human, and the later ones are just the result of mixing from back migration.
When Klevius in the 1980s got in contact with African aborigines he immediately was struck by their mongoloid appearance. Why on earth would African aborigines have traces of cold adaptation? Today we have the answer in Siberia.
Klevius wrote:
Monday, October 22, 2018
John Hawks again missed (since 1992 in a book and since 2003 on the web) Klevius' original science contribution re. social evolution of human societies.
Among serious anthropologists John Hawks' blog is the most read while Peter Klevius' blog is the least* read. Why? Is it because of Klevius' "Saudiphobia"/"islamo(fascism)phobia"?
* So have patience with Klevius self-citations (and do read the chapter Science and References in Demand for Resources) which clearly are more important for general science than for Klevius own satisfaction.See Klevius 1992:40-44.
Richard Lee's The !Kung San: Men, Women, and Work in a Foraging Society came 1979 and was the main trigger of Klevius first letter to Georg Henrik von Wright (Wittgenstein's successor at Cambridge) on the topic and Klevius 1981 article Demand for Resources and 1992 book with the same title.
Out of respect and as support for Lee's work Klevius also bought the expensive Cambridge Encyclopedia of Hunter-Gatherers (1999), which, of course, was of no practical use for Klevius.
Here's John Hawks recent blog-post:
Hawks writes:
He (Lee) has written an article in this year’s Annual Review of Anthropology that examines both uses and misuses of hunter-gatherer ethnography in theory-building about human nature: “Hunter-Gatherers and Human Evolution: New Light on Old Debates.”
In the introduction to the article, he recounts a story involving his “Man the Hunter” co-editor, the late Irven DeVore:
Senator William Fulbright of Arkansas, a brilliant US legislator in the 1960s and the founder of the scholarship program that bears his name, was just one public figure struggling to come to grips with the import of Lorenz’s theses. I vividly remember the late Irven DeVore coming into my office at Harvard University. “I just got off the phone with Senator William Fulbright calling from Washington,” Devore said. “He asked me ‘Professor DeVore, if Konrad Lorenz is right, how are we ever to negotiate a nuclear arms reduction treaty with the Soviet Union?’”
DeVore reassured Fulbright that Lorenz’s views were far from universally accepted among anthropologists, that violence in human history was a variable not a constant, and that its causes and expressions were far more complex than could be explained simply by pure animal instinct.
DeVore’s disclaimers appeared to calm Senator Fulbright’s nerves, and in fact the United States and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) went on to successfully negotiate a series of nuclear arms reduction treaties over the years. Nevertheless, the question of violence in human history continued to animate the debate within anthropology, fueled by Robert Ardrey’s “killer ape” hypothesis in his books African Genesis (Ardrey 1961) and The Territorial Imperative (Ardrey 1966). Interest was sustained by Napoleon Chagnon’s (1968) influential ethnography of the “fierce” Yanomamo and more recently by the writings of Wrangham & Peterson (1996), such as Demonic Males: Apes and the Origins of Human Violence. I have labeled this persistent thread within anthropology and related disciplines as the “Bellicose School” (Lee 2014).
I am spending some time reading this review and taking notes, and it bears close reading. Lee’s theme is that many people who use “hunter-gatherers” as a category are actually lumping things that are quite different from each other. If you want to use ethnographic studies of today’s people to say anything about prehistoric people, you need to understand that any living group may be like ancient people in some ways, and very different from ancient people in other ways.
Klevius writes: When it comes to Konrad Lorentz I share Lee's view - as clearly stated on page 20 in Demand for Resources (1992):
Det finns ett flertal delikata kulturantropologiska fördomar som fått starka grepp på allmänheten. En sådan gäller föreställningen om människans aggressivitet som en oemotståndlig negativ biologisk kraft som måste få utlopp. Att hävda detta och samtidigt förorda kanaliserad aggressivitet i syfte att förmildra verkningarna av densamma innebär i själva verket att man kulturellt skapar och stimulerar beteendemönster av negativ karaktär. Fysiskt våld mot artfränder är liksom utvidgat resursbegär en inlärd egenskap. Den organiserade form av fysiskt våld mot artfränder som krig innebär verkar inte vara äldre än det utvidgade resursbegäret. Troligen hänger de intimt samman.
And translated from original English, i.e. Swedish, to modern English:
There are several delicate cultural-anthropological prejudices which have got a strong grip on the public. One is the view about human aggression as an irresistible negative biological force which has to be released. To argue this while simultaneously proposing channeled aggressiveness for the purpose of mitigating its effects, in fact, means that one culturally creates and stimulates patterns of negative behavior. Same species violence is, like expanded demand for resources, a learned behavior. The organized form of violence, i.e. war, seems not to be older than expanded demands for resources. They are likely intimately connected.
Demand for Resources by Peter Klevius (1992).
The civilized wo/man walks
back in her/his foot steps,
strikes a light and lets her/himself be enlightened
and glorified
Only the forgotten suffering,
and the shadow behind her/him,
hovering over the future,
are greater (P. Klevius 1992, title page).
"The archeologist of knowledge finds
in his/her digging
often him/herself"
(P. Klevius 1992:7)
The concept of freedom is created,
like diamonds,
only under pressure
(P. Klevius 1992:33)
More from Demand for Resources (1992, ISBN 9173288411):
So called civilized societies can be described as dynamic, hence contrasting against the more static appearance of the economic setting (lack of investment) of e.g. hunter-gatherers.
A re-classification of human societies departing from C. Levi-Strauss idea about "warm" and "cold" societies (Klevius 1992):
A Without 'extended demands for resources' (EDFR).
B Affected by EDFR but still retaining a simplistic, "primitive" way of life.
C Civilized with EDFR
These categories are, of course, only conceptual. Applied to a conventional classification the following pattern appears:
1 The primitive stage when all were hunter/gatherers (A, according to EDFR classification).
2 Nomads (A, B, C).
3 Farmers (B, C).
4 Civilized (C).
As a consequence EDFR is here used as a concept tied to civilization (and its preliminary stages) The above also suggests a critique against our conventional conception of a simplistic connection between intelligence and performance as (wrongly) exemplified by C. Popper's scenario of a World 1-3 transition of human cultural development.
(Implications of this view can be seen in Klevius theory of mind EMAH, The Even More Astonishing Hypothesis, which deals with the mind/body "problem" and the closing gap between not only humans and other living things but also betweenhumans and machines).
Here's the last part of the chapter Khoe, San and Bantu (in Demand for Resources, Klevius 1992).
For those who don't master original English there are some modern English words as well in the text:
I begreppet San inryms de tre grupperna !Kung, !Xu och G!wi vilka alla har egna närbesläktade men självständiga språk. Av dessa grupper är det G!wi som kan antas stå närmast det klassiska samlar/jägarsamhället även om egentligen inga grupper i dag återfinns i de kulturmönster som förekom ännu på 50-60-talet.
En uppskattning av de traditionella egenskaperna i kulturmönstret hos San (konventionellt grupp 1, URB-grupp A) inkluderar frånvaro av domesticering, lös sammanhållning, ofixerad, icke hierarkisk beslutsordning samt i det närmaste obefintlig materiell status (undantag utgör t.ex. jaktvapen och byten före den oundvikliga fördelningen).
Patricia Draper har i anslutning till "The Harvard !Kung Bushmen Study Project" gjort en undersökning om skillnader i könsroller hos kringvandrande klassiska samlar/jägargrupper och stationära "mångsysslande" !Kung grupper. Hon fann då bl.a. "that !Kung society may be the least sexist of any we have experienced" samt att detta märks genom "women's subsistence contribution and the control women retain over the food they have gathered, the lack of rigidity in sex-typing of many adult activities including domestic chores and aspects of child socialization; the cultural sanction against physical expression of aggression; the smaller group size; and the nature of the settlement pattern." Hon noterar vidare att "authoritarian behavior is avoided by adults of both sexes." Alla dessa egenskaper naggades enligt Draper i kanten hos de stationära grupperna.
En pionjär då det gällde att påvisa hur lite arbete som San samlar/jägarna lade ner på födoanskaffning och boende var Richard Lee som 1963 studerade den bland antropologer numera välkända Dobe Base Camp 12. Han levde med dem, noterade metodiskt allt han såg, mätte och vägde såväl mat som människor, tog tid på allt de gjorde och resultatet av hans, och senare även andras arbeten kan sammanfattas i Marshal Sahlins ord: "If the affluent society is one where all the people's material wants are easily satisfied this is the first affluent society." Han fortsatte: "The human condition must keep man the prisoner at hard labor of a perpetual disparity between his unlimited wants and his insufficient means... " och vidare "There is (instead) a road to affluence, departing from premises... that human wants are few, and technical means unchanging but on the whole adequate."
I mitten av 70-talet kunde bl.a. Diane Gelburd konstatera att bushmännens liv i Dobe hade ändrat karaktär sedan Richard Lee's fältstudier. Hyddorna var byggda av lera istället för av gräs och stod längre ifrån varandra. En del fick dörrar i takt med att de fylldes med personliga ägodelar. Man byggde stängsel för djuren som man nu införskaffat. Likadant var det med benresterna som tidigare enbart bestått av lämningar från vilda djur men 1976 till 80% bestod av benrester från domesticerade djur.
Samtidigt skedde förändringar i de interna sociala relationerna. Fördelning av tillgångar minskade och formerna för t.ex. äktenskap komplicerades p.g.a. nya, förut okända problem kring egendomsfrågor.
"What explains the shattering of this society"? frågade sig John Yellen från The National Science Foundation anthropology program. Han fortsätter: "It hasn't been a direct force, a war, the ravages of disease..." och svarar slutligen: "1t is the internal conflicts, the tensions, the inconsistencies, the impossibility of reconciling such different views of the world."
Till detta kan tilläggas att Khoi och San har levt i flera tusen år sida vid sida utan att de samlande/jagande San blivit boskapshållare. Dessutom har de jordbrukande ochboskapsskötande Bantufolken för åtminstone 500 år sedan invaderat Khoisan?folkens traditionella marker.
Det är alltså något mer som skall till för att knäcka ryggraden på ett typiskt San-samhälle. Handlar det om en kritisk punkt för försörjningsunderlag/befolkningsstorlek? Finns det en nedre gräns för antalet individer i en fungerande samlar/jägarkultur? I vilket skede exakt bryts det sociala immunförsvaret gentemot utvidgade resursbegär ner?
Oavsett om det finns en kritisk punkt eller om det är fråga om en långsamt ökande spänning som efter hand får det ena fästet efter det andra att ge efter så ser vi här uppkomsten av den spricka mellan kulturformer där det utvidgande resursbegäret med varierande framgång slagit rot.





































































































































































No comments:
Post a Comment